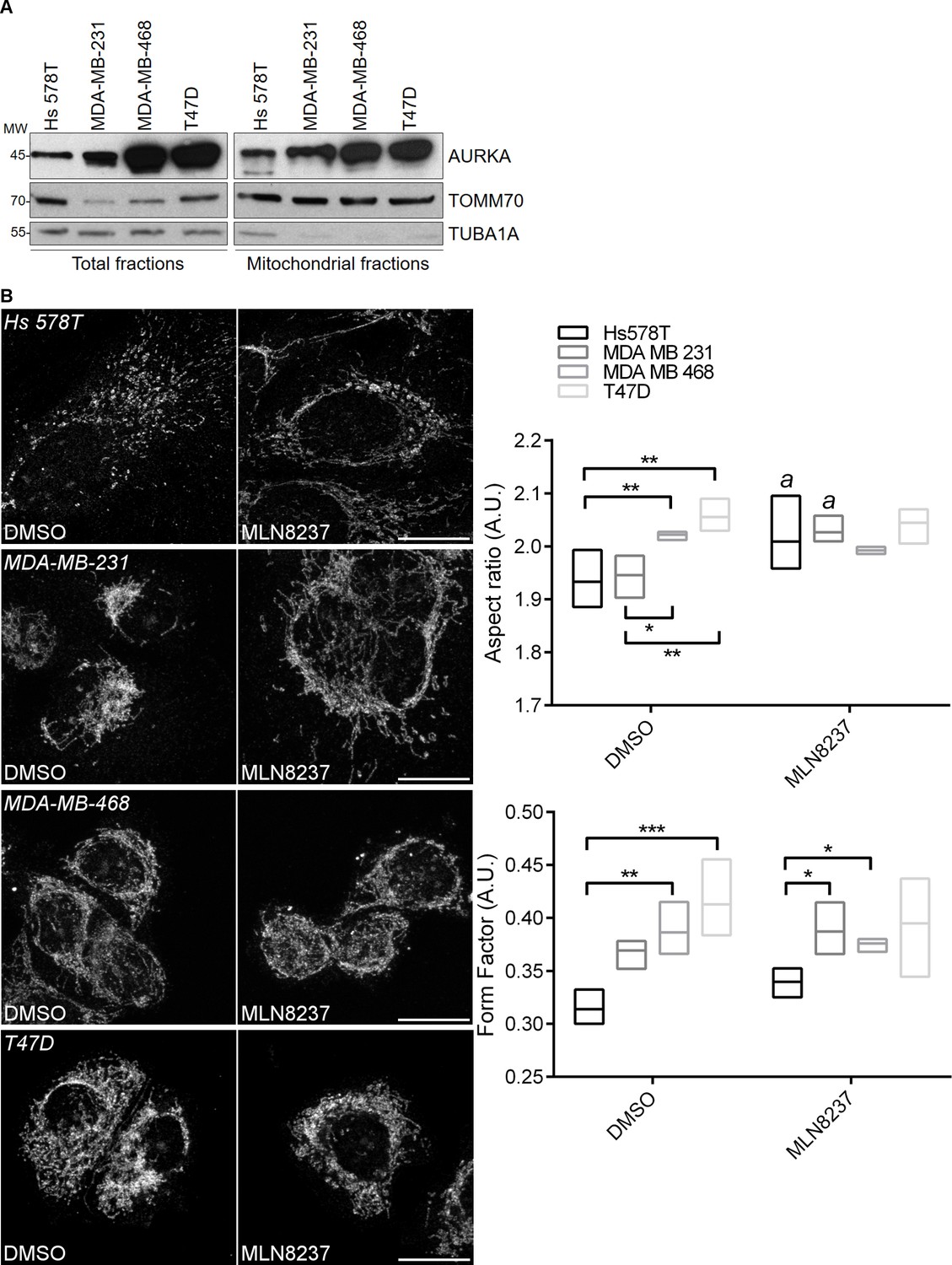
B localize to key mitotic structuresSubcellular Biology Diagrams Aurora A is localized to spindle poles where it provides spatial information for spindle functions in prometaphase. Aurora A is a kinase that is highly related to Aurora B but the two kinases localize to distinct subcellular regions during mitosis . From prometaphase to anaphase Aurora A localizes to the two poles of the spindle, which are the

Aurora kinases, which have been implicated in several vital events in mitosis, represent a protein kinase family highly conserved during evolution. Aurora kinases are serine/threonine kinases essential for the onset and progression of mitosis. Aurora members share a similar protein structure and kinase activity, but exhibit distinct cellular and subcellular localization. AurA favors the G2/M transition by promoting centrosome maturation and mitotic spindle assembly. AurB and AurC are chromosome-passenger complex proteins, crucial for

Aurora kinases: structure, functions and their association ... Biology Diagrams
During mitosis, Aurora kinases regulate the structure and function of the cytoskeleton and chromosomes and the interactions between these two at the kinetochore. They also regulate signalling by

As described above, there are three classes of aurora kinases in multicellular organisms, including humans: Aurora A (a.k.a. Aurora 2) functions during prophase of mitosis and is required for correct duplication and separation of the centrosomes (the microtubule organising centres in eukaryotic cells). Aurora A activity is positively-regulated by the spindle protein TPX2, [4] [5] and has
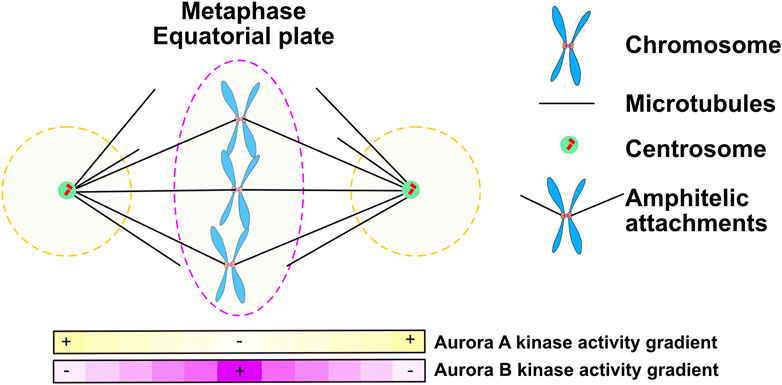
Aurora kinases: Current Biology Biology Diagrams
These inhibitors obstruct Aurora kinases, which in turn leads to aberrant mitosis. As a result, the p53-dependent checkpoint is activated and results in the induction of a G1-like cell-cycle arrest. Several small-molecule inhibitors of Aurora kinases, such as VX-680, PHA-739358 and AZD-1152, have shown anti-cancer effects in preclinical and